Mastering the Art of AI Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Prompt Engineering in 2025
Discover the depths of prompt engineering, from basic definitions and historical evolution to advanced frameworks like COSTAR and CRISPE. Learn how to craft perfect prompts for text, images, and video.

The New Literacy: Why AI Communication Matters
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the 21st century, a new form of literacy has emerged. Just as the industrial revolution required a mastery of machinery and the digital revolution demanded basic computer skills, the AI era requires mastery over the 'prompt.' At its core, prompt engineering is the art and science of communicating effectively with artificial intelligence. It is the bridge between human intent and machine execution. Whether you are a developer, a creative, or a business professional, understanding how to 'whisper' to AI is becoming a non-negotiable skill. At Xerpihan, we believe that empowering users with these tools is essential for navigating the future of technology and language services.

What is a Prompt?
A prompt is simply the input provided to an AI model to elicit a specific response. It can be a single word, a question, a block of code, or a complex set of instructions. In the context of Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or Claude, the prompt acts as the 'initial condition' for the model's probabilistic generation process. When you give an AI a prompt, you are not just asking a question; you are setting the boundaries of its creative space. You are defining the tone, the context, and the constraints that will shape the final output.
The Anatomy of a Prompt
To understand a prompt, we must look at its components. A high-quality prompt typically includes four key elements: instruction (the specific task), context (background information), input data (the information the AI needs to process), and output indicators (the desired format). By balancing these four pillars, a user can transform a generic, 'hallucination-prone' AI into a precise, professional assistant.
The Evolution of Interaction: From ELIZA to Transformers
The history of prompting is a fascinating journey through computer science. It began in the 1960s with ELIZA, a primitive chatbot that used simple pattern matching to simulate human conversation. For decades, 'prompting' a computer meant typing rigid, syntax-heavy commands into a terminal. However, the 2017 'Attention Is All You Need' paper introduced the Transformer architecture, which changed everything. This allowed models to process language with a deep understanding of context and relationships. By 2024 and 2025, we have moved into the era of 'Dynamic Prompt Systems' and 'Multimodal Interfaces,' where prompts are no longer just text but a combination of voice, images, and even real-time feedback loops.
What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the systematic process of refining and optimizing prompts to improve the performance of AI models. It is more than just 'writing instructions'; it is a discipline that involves psychology, linguistics, and logic. A prompt engineer seeks to understand the 'latent space' of a model—the hidden connections between concepts that the AI has learned during training. By applying specific techniques, engineers can minimize bias, reduce hallucinations (the generation of false information), and unlock hidden capabilities of the model that aren't immediately apparent through basic interaction.
Why Structure Beats Spontaneity
One of the most important lessons in prompt engineering is that structure beats spontaneity. Vague prompts lead to vague results. For example, asking an AI to 'Write a blog' is a weak prompt. A structured prompt would be: 'Act as a professional technology journalist. Write a 1,500-word deep-dive article about the impact of quantum computing on cybersecurity for a non-technical audience. Include three case studies and use a professional yet accessible tone.' The latter provides the AI with a roadmap, ensuring the output matches the user's vision.
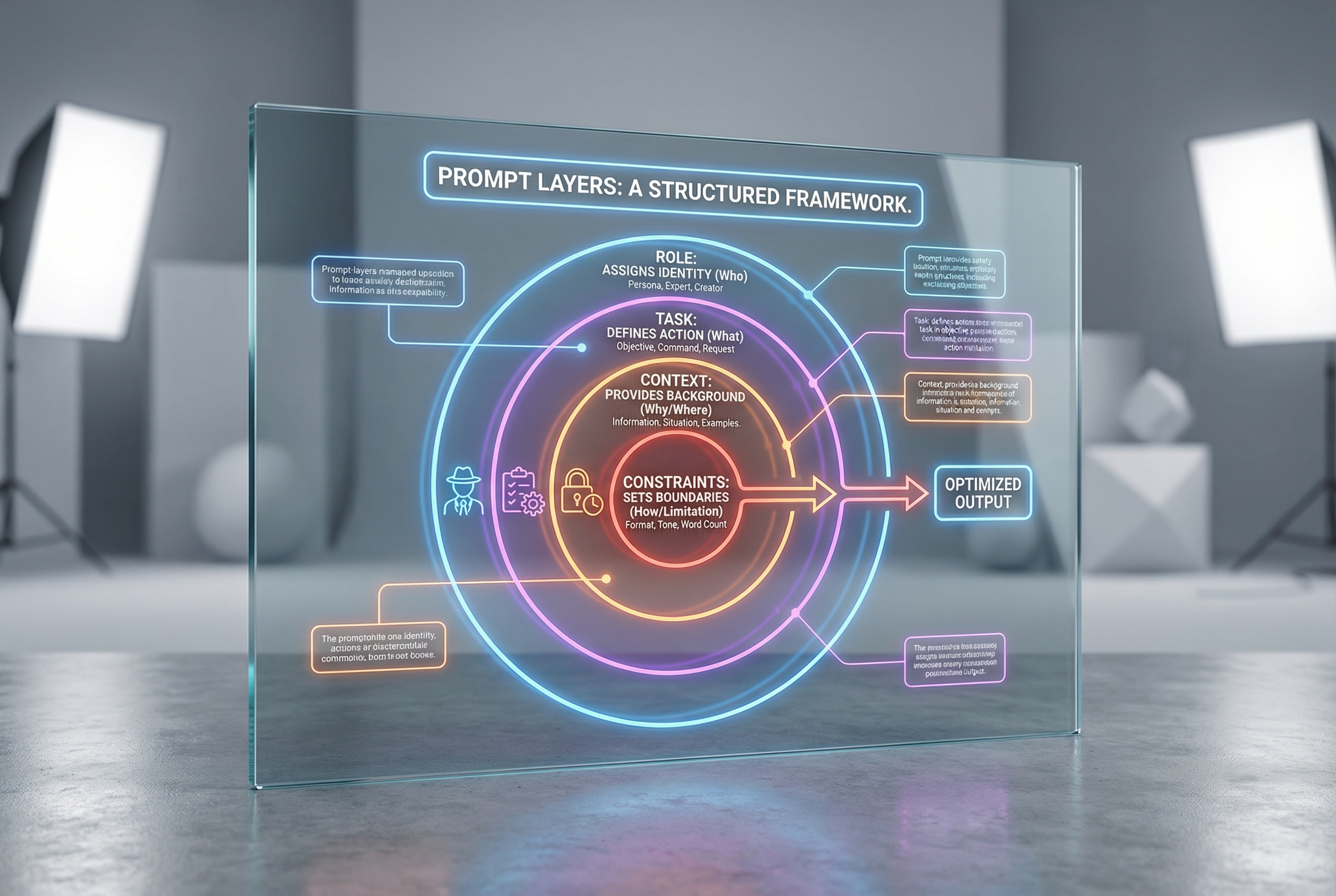
Advanced Prompt Frameworks: COSTAR and CRISPE
To help users move beyond basic questioning, several frameworks have been developed. These provide a 'fill-in-the-blank' structure that guarantees high-quality results.
- COSTAR Framework: Context (the background), Objective (the goal), Style (the persona), Tone (the emotion), Audience (the target), and Response (the format).
- CRISPE Framework: Context, Role, Input, Steps (the workflow), Parameters (constraints), and Examples (few-shot prompting).
- RTF Framework: Role, Task, and Format. This is the 'Swiss Army Knife' of prompting, perfect for daily tasks.
Types of Prompts and Their Applications
As AI becomes more sophisticated, different 'types' of prompting have emerged to solve specific problems.
Zero-Shot vs. Few-Shot Prompting
Zero-shot prompting is asking a model a question with no examples. It relies entirely on the model's pre-existing knowledge. Few-shot prompting, on the other hand, involves giving the AI 2-3 examples of the desired output. This is significantly more effective for maintaining a specific brand voice or a complex formatting style.
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Prompting
This technique involves asking the AI to 'think step-by-step.' By forcing the model to articulate its reasoning before reaching a conclusion, you dramatically improve its accuracy in logic, math, and coding tasks. In 2025, 'Tree-of-Thoughts' and 'ReAct' (Reason + Act) have taken this further, allowing AI to branch its reasoning and interact with external tools to verify facts.
How to Learn Prompting: A Step-by-Step Guide
Learning prompt engineering is an iterative process. It is not about memorizing commands but about developing a 'feel' for the model.
- Step 1: Start with the Persona. Always tell the AI who it should be. 'Act as a Senior SEO Specialist' or 'Act as a Creative Director.'
- Step 2: Define the Boundaries. Tell the AI what NOT to do. Use negative prompts like 'Do not use jargon' or 'Avoid passive voice.'
- Step 3: The Iteration Loop. Never settle for the first result. Use 'Prompt Tuning'—take the output, identify what's missing, and refine the instructions.
- Step 4: Use Examples. If you want a specific style, paste an example of your previous writing into the prompt.
Real-World Examples: Video, Image, and Article Prompts
To truly master this, we must look at how prompts differ across mediums.
Example: Article Prompt
'Act as a data analyst. Based on the attached CSV file of sales data, write a report that identifies the top 3 growth opportunities for 2025. Use a formal tone and present the final output in a markdown table followed by a 500-word analysis.'
Example: AI Video Prompt
'Subject: A futuristic humanoid robot. Action: Walking through a rain-slicked neon street in Tokyo. Camera: Low-angle tracking shot, slow-motion. Lighting: High-contrast cinematic lighting with blue and magenta hues. Style: Cyberpunk, hyper-realistic, 8k resolution.'
Example: AI Image Prompt (Daily Life)
'A medium shot of a young professional woman sitting in a sunlit home office, she is focused on her laptop screen, a half-empty ceramic coffee mug sits on a wooden desk next to a small succulent plant, soft morning light filtering through linen curtains, high-quality photography, realistic skin textures, 35mm lens style.'

Conclusion: The Future of AI Communication
As we look toward the future, prompt engineering will continue to evolve. Some experts predict that AI models will become so intuitive that 'engineering' will no longer be necessary—we will simply speak to machines as we do to humans. However, the ability to think clearly, structure instructions logically, and provide meaningful context will always be valuable human traits. At Xerpihan, we encourage you to start experimenting today. The prompt is your brush, and the AI is your canvas. What will you create next?


